Tag: chemistry

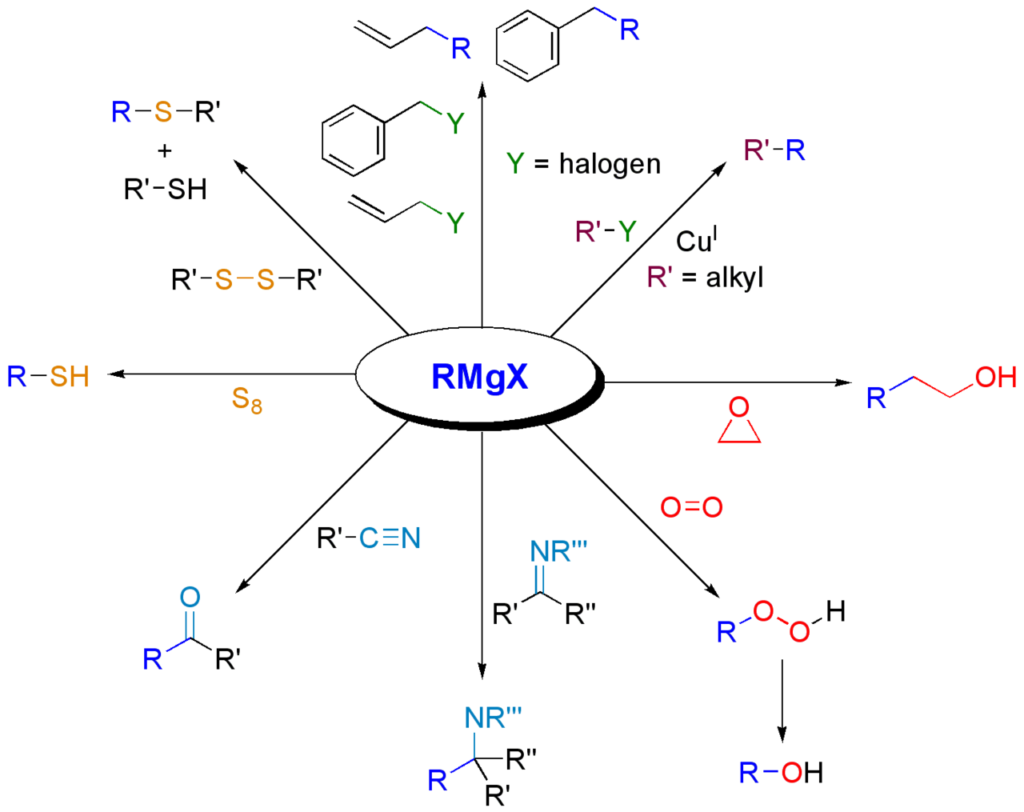
Grignard Reagent: Reactions, Preparations, and Beyond
Grignard reagents, named after the French chemist Victor Grignard who discovered them, are a class of organometallic compounds used in organic chemistry for various chemical reactions.

Heck Reaction: Catalysts, Substrates, and Scope
The Heck reaction, named after the American chemist Richard F. Heck who developed it in the 1960s, is a widely used chemical reaction in organic chemistry. It is a powerful method for forming carbon-carbon (C-C) bonds to create substituted alkenes (olefins) from aryl or vinyl halides and an alkene in the presence of a palladium…

Dansyl Chloride: Properties and Applications
Dansyl chloride is a chemical compound often used in analytical chemistry and biochemistry as a fluorescent labeling agent. It is a derivative of the organic compound dansylamine and is known for its ability to react with amino groups in proteins and other biomolecules, forming stable fluorescent derivatives.

Hofmann Rearrangement: Understanding its Mechanism and Applications
The Hofmann rearrangement, named after its discoverer August Wilhelm von Hofmann, is a chemical reaction used to convert primary amides into primary amines with one fewer carbon atom.

Beckmann Rearrangement: Mechanisms, Applications, and Innovations
The Beckmann rearrangement is a chemical reaction that involves the conversion of an oxime functional group into an amide functional group. This rearrangement is named after the German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann, who first described it in the late 19th century.

Curtius Rearrangement: Mechanisms, Variations, and Implications
The Curtius rearrangement, named after the German chemist Theodor Curtius, is a chemical reaction that involves the conversion of a carboxylic acid into an isocyanate compound.

Aldol Condensation
Aldol condensation is a chemical reaction that involves the combination of two molecules of aldehyde or ketone compounds to form a larger molecule. This reaction is a fundamental process in organic chemistry and is named after its two primary reaction products, aldehydes and ketones, and the term “aldol” is a combination of “aldehyde” and “alcohol.”

Edman Degradation
Edman Degradation is a widely used chemical method for determining the amino acid sequence in a peptide or protein. This technique was developed by the Swiss chemist Pehr Edman in the 1950s and has since been a fundamental tool in the field of biochemistry.

Birch Reduction
Birch reduction is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry to reduce aromatic compounds, typically benzene rings, by adding electrons and protons. This reaction is named after the American chemist Gilbert N. Lewis, who first proposed the mechanism, and the British chemist Sir Arthur Birch, who later popularized and developed the reaction.